FREE SHIPPING OVER $50
Stop Buying the Wrong Milk: These 10 Options Are Healthiest and Highest in Protein
Navigating the dairy aisle can be overwhelming with the plethora of milk options available today. From traditional cow’s milk to a variety of plant-based alternatives, choosing the right milk to meet your health and protein needs is crucial. This guide ranks the top 10 healthiest and highest-protein milk types to help you make informed choices.
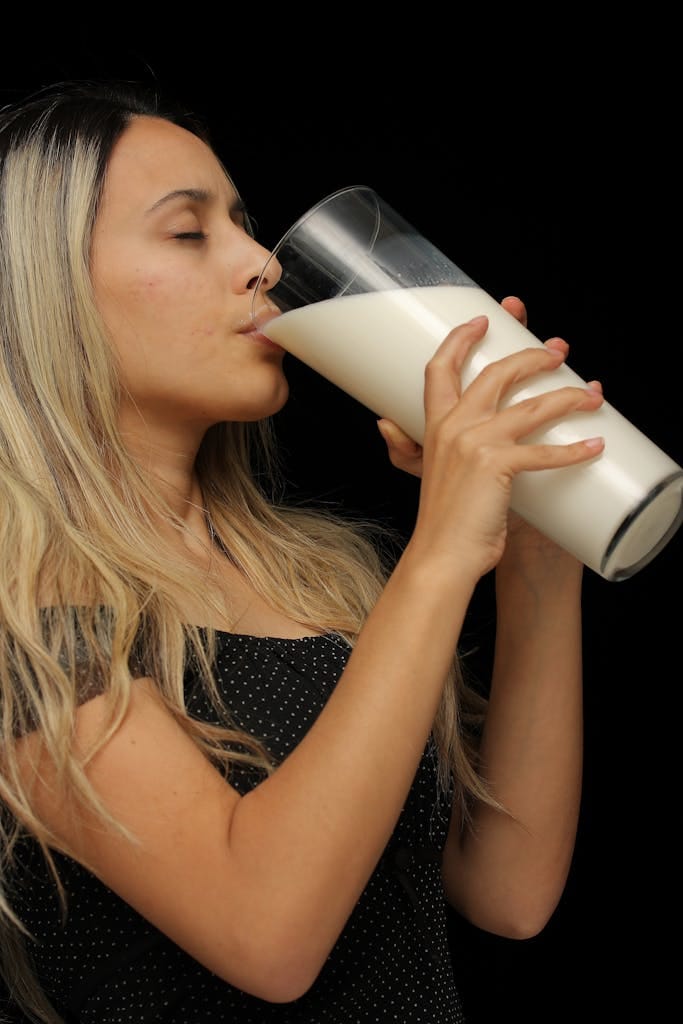

1. Cow’s Milk (2% Reduced Fat): The Gold Standard
Cow’s milk remains a staple in many diets due to its rich nutrient profile. A one-cup serving of 2% reduced-fat cow’s milk provides approximately 8.23 grams of high-quality protein, along with essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and B vitamins. It’s an excellent choice for those not lactose intolerant and seeking a natural source of protein and other vital nutrients.
2. Soy Milk: Plant-Based Powerhouse
Soy milk stands out among plant-based alternatives for its high protein content, offering around 8.86 grams per cup. It’s a complete protein source, containing all essential amino acids, and is often fortified with calcium and vitamin D. Soy milk is an excellent option for vegans and those with dairy allergies.
3. Pea Milk: Allergen-Friendly and Protein-Rich
Pea milk, made from yellow peas, provides approximately 8 grams of protein per cup. It’s free from common allergens like dairy, soy, and nuts, making it suitable for various dietary restrictions. Additionally, pea milk is often fortified with calcium and vitamin D, supporting bone health.
4. Skim Milk: Low-Fat, High-Protein
Skim milk offers the same protein content as whole milk—about 8 grams per cup—but with significantly less fat and fewer calories. It’s an ideal choice for those looking to reduce fat intake while maintaining protein consumption.
5. Fortified Almond Milk: Enhanced Plant-Based Option
Standard almond milk is low in protein, typically around 1 gram per cup. However, fortified versions, such as Silk’s Protein Almond Milk, can provide up to 10 grams of protein per serving. These enhanced options combine almond milk with added plant proteins, offering a higher-protein alternative for those preferring almond milk’s taste and texture.
6. Hemp Milk: Omega-3s and Moderate Protein
Hemp milk delivers about 3 grams of protein per cup and is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health. It’s also a good source of calcium and iron, making it a nutritious choice for those seeking plant-based options with additional health benefits.
7. Oat Milk: Creamy Texture with Added Fiber
Oat milk provides approximately 3 grams of protein per cup and contains beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber that can help lower cholesterol levels. While not as high in protein as other options, its creamy texture and added fiber make it a popular choice for lattes and smoothies.
8. Cashew Milk: Creamy and Nutrient-Rich
Cashew milk offers around 4 grams of protein per cup and is known for its creamy consistency. It’s also a source of healthy fats and can be fortified with calcium and vitamin D, supporting bone health.
9. Lactose-Free Milk: Dairy Without the Discomfort
Lactose-free milk provides the same protein content as regular cow’s milk—about 8 grams per cup—without the lactose, making it suitable for those with lactose intolerance. It’s often fortified with additional nutrients, ensuring you don’t miss out on essential vitamins and minerals.
10. Flax Milk: Low-Calorie and Fortified
Flax milk is typically low in protein, around 1 gram per cup, but fortified versions can offer higher protein content. It’s a good source of omega-3 fatty acids and is often enriched with calcium and vitamin D, making it a heart-healthy, plant-based alternative.
Conclusion
Choosing the right milk depends on your dietary needs, taste preferences, and nutritional goals. Whether you prefer traditional dairy or plant-based alternatives, options like cow’s milk, soy milk, and fortified plant milks can help you meet your protein requirements while supporting overall health. Always check labels for added sugars and fortification to ensure you’re making the healthiest choice for your lifestyle.
Related Articles
- Milk vs. Water for Protein Shakes: Which Helps Build More Muscle?
- We Tried 17 Protein Powders—These 7 Are Actually Worth Your Money
- Top FODMAP-Friendly Protein Powders and Meal Replacements You Need Now
- Try These 5 High-Protein Smoothie Ingredients Instead of Protein Powder
- This High-Protein Snack Can Help Lower Your Cholesterol, Say Dietitians