FREE SHIPPING OVER $50
What is Diffuse Thinning and How to Stop It
Hair loss is a common concern for many people, but understanding the specifics of different types of hair loss can be confusing. One such type is diffuse thinning. This condition can be distressing, but with the right knowledge and approach, it can be managed. In this article, we’ll explore what diffuse thinning is, its causes, signs and symptoms, and effective strategies to stop it.
Key Takeaways
What is Diffuse Thinning?
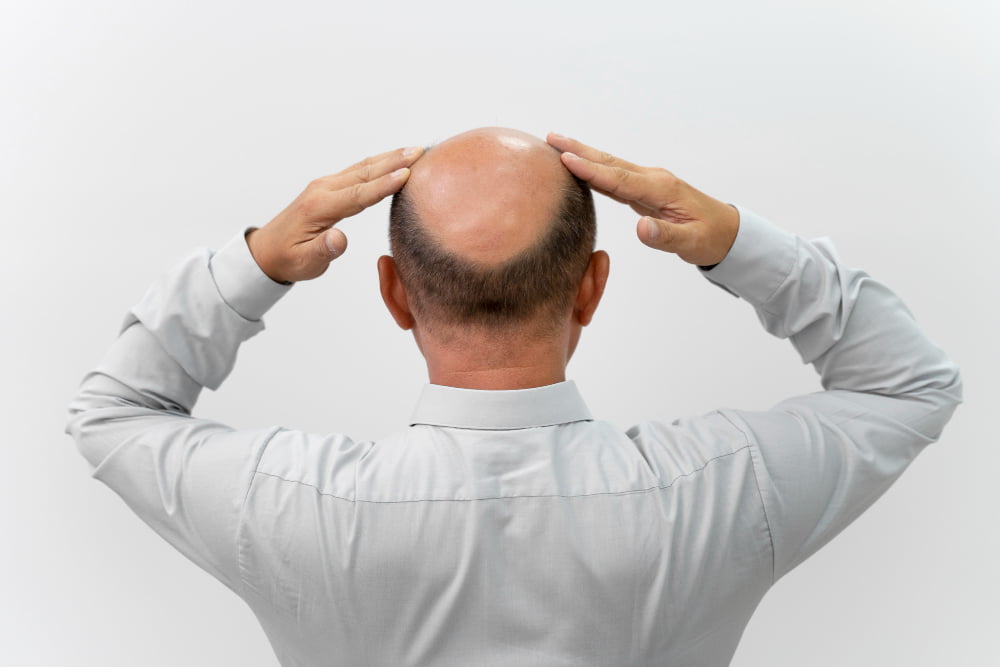

Diffuse thinning refers to an overall reduction in hair density, affecting the entire scalp rather than specific areas. This type of hair loss is often uniform, making it less noticeable initially compared to pattern baldness. Unlike localized bald spots, diffuse thinning results in hair that appears thin and sparse all over the head.
Causes of Diffuse Thinning
Understanding the causes of diffuse thinning is crucial for addressing it effectively. Several factors can contribute to this condition, including:
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is one of the most common causes of diffuse thinning. It occurs when a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting (telogen) phase simultaneously, leading to widespread shedding. This condition can be triggered by severe stress, major surgery, illness, or hormonal changes. Although telogen effluvium is usually temporary, it can cause noticeable thinning if not addressed promptly.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Lack of essential vitamins and minerals can weaken hair follicles, leading to diffuse thinning. Nutrients like iron, zinc, and biotin are crucial for healthy hair growth. A deficiency in these nutrients can disrupt the hair growth cycle, causing increased shedding and reduced hair density.
Hormonal Imbalances
Conditions such as thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can contribute to diffuse thinning. Hormonal fluctuations can affect the hair growth cycle, leading to increased shedding and thinning.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can cause diffuse thinning. Alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder, can lead to patchy hair loss and, in some cases, diffuse thinning. Chronic illnesses like diabetes, lupus, and scalp infections can also impact hair density.
Medications
Some medications have side effects that include hair thinning. Chemotherapy drugs are well-known for causing hair loss, but other medications like blood thinners, antidepressants, and beta-blockers can also contribute to diffuse thinning.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in hair loss patterns. While the Norwood scale is typically used to measure male pattern baldness, it’s important to note that genetic predisposition can also influence diffuse thinning in both men and women. If your family has a history of hair loss, you may be more prone to experiencing diffuse thinning.
Signs and Symptoms of Diffuse Thinning
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of diffuse thinning early is key to managing it effectively. Here are common indicators:
- Overall Thinning: A noticeable reduction in hair volume across the entire scalp.
- Increased Shedding: More hair loss than usual when brushing or washing hair.
- Scalp Visibility: Increased visibility of the scalp, particularly when the hair is wet or parted.
- Loss of Hair Density: Hair feels lighter and less dense to the touch.
- Brittle Hair: Hair may become weaker and more prone to breakage.
One way to notice this condition is by examining your hair when it’s wet. Wet diffuse thinning is often more noticeable because wet hair clumps together, making thin areas more apparent. Regularly checking your hair density, especially after washing, can help you spot early signs of diffuse thinning.
Is Diffuse Thinning Reversible?
A common question is “Is diffuse thinning reversible?” The answer depends on the underlying cause. If the thinning is due to temporary factors like stress or nutritional deficiencies, addressing these issues can lead to hair regrowth. However, if the thinning is caused by genetic factors, managing the condition may require ongoing treatment.
Effective Strategies to Stop Diffuse Thinning
There are several strategies to combat diffuse thinning and promote hair health:
1. Improve Your Diet
Nutrition plays a vital role in hair health. Ensure your diet includes:
- Protein: Hair is primarily made of protein, so a protein-rich diet is essential.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Incorporate foods rich in iron, zinc, vitamin D, and biotin.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your hair hydrated and healthy.
2. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can exacerbate hair thinning. Techniques to manage stress include:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps reduce stress levels.
- Meditation and Yoga: These practices promote relaxation and mental well-being.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get 7-9 hours of sleep per night to help your body recover from daily stress.
3. Hair Care Routine
Adopt a hair care routine that promotes scalp health and hair growth:
- Gentle Shampooing: Use mild shampoos and avoid harsh chemicals.
- Scalp Massage: Regular scalp massages can increase blood flow to hair follicles.
- Avoid Heat Styling: Minimize the use of hairdryers, straighteners, and curling irons to prevent damage.
Medical Treatments for Diffuse Thinning
For more persistent cases of diffuse thinning, medical treatments might be necessary:
1. Medications
- Minoxidil: An over-the-counter topical treatment that can stimulate hair growth.
- Finasteride: A prescription medication that can slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
- Spironolactone: A medication that can help reduce hair loss in women by addressing hormonal imbalances.
- Corticosteroids: Topical or injectable steroids that can reduce inflammation and promote hair growth, particularly in cases of alopecia areata.
2. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting the patient’s own platelet-rich plasma into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. This treatment leverages the growth factors in the plasma to promote healing and rejuvenation of hair follicles.
3. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT uses red light wavelengths to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. This non-invasive treatment can be done at home with a laser cap or in a clinical setting.
4. Hair Transplants
A diffuse thinning hair transplant is a surgical option where hair follicles are transplanted from denser areas to thinning areas. This can be an effective solution for those with significant hair loss.
Home Remedies for Diffuse Thinning
For those seeking natural approaches to manage diffuse thinning, several home remedies can be effective:
- Essential Oils:
- Rosemary Oil: Known for stimulating hair growth, rosemary oil can be massaged into the scalp.
- Peppermint Oil: This oil can increase blood circulation to the scalp and promote hair growth.
- Lavender Oil: It helps in deep conditioning the hair and keeping it shiny.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has soothing properties and can help reduce scalp inflammation, which can promote healthy hair growth. Apply aloe vera gel directly to the scalp and let it sit for about an hour before washing it off.
- Onion Juice: Onion juice is rich in sulfur, which is beneficial for hair growth. Applying onion juice to the scalp can enhance blood circulation and boost hair growth. Leave it on for about 15-20 minutes before washing it off with a mild shampoo.
- Green Tea: Green tea is rich in antioxidants which can help prevent hair loss and stimulate growth. Brew a few tea bags in hot water, let it cool, and then rinse your hair with this solution.
- Coconut Oil: Coconut oil can penetrate the hair shaft and prevent protein loss. Massaging warm coconut oil into your scalp can help nourish hair and promote growth. Leave it on for at least an hour, or overnight, before washing it off.
However, while these remedies can potentially help, they are not guaranteed to work for everyone and are not a substitute for medical treatment. It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment regiment
Wet Diffuse Thinning and Hair Transplants
When considering a hair transplant, it’s important to address wet diffuse thinning. Wet hair can reveal the true extent of thinning, helping doctors plan the transplant more accurately. Discussing your hair condition, including how it appears when wet, with your doctor can lead to a more effective treatment plan.
Conclusion
Understanding what diffuse thinning is and how to stop it is essential for managing this condition. By addressing underlying causes, improving your diet, managing stress, and adopting a healthy hair care routine, you can combat diffuse thinning. For more severe cases, medical treatments and hair transplants can offer solutions.